Engaging in physical exercise is a fundamental aspect of maintaining good health, enhancing physical performance, and improving overall quality of life. However, with the increasing popularity of fitness activities, the risk of workout injuries has also risen significantly. Whether you are a seasoned athlete or a casual gym-goer, understanding how to avoid common workout injuries is crucial for ensuring a safe and effective exercise regimen. This comprehensive guide will explore the types of workout injuries, their causes, prevention strategies, and steps to take in case of an injury, empowering you to stay safe while pursuing your fitness goals.
Understanding Common Workout Injuries
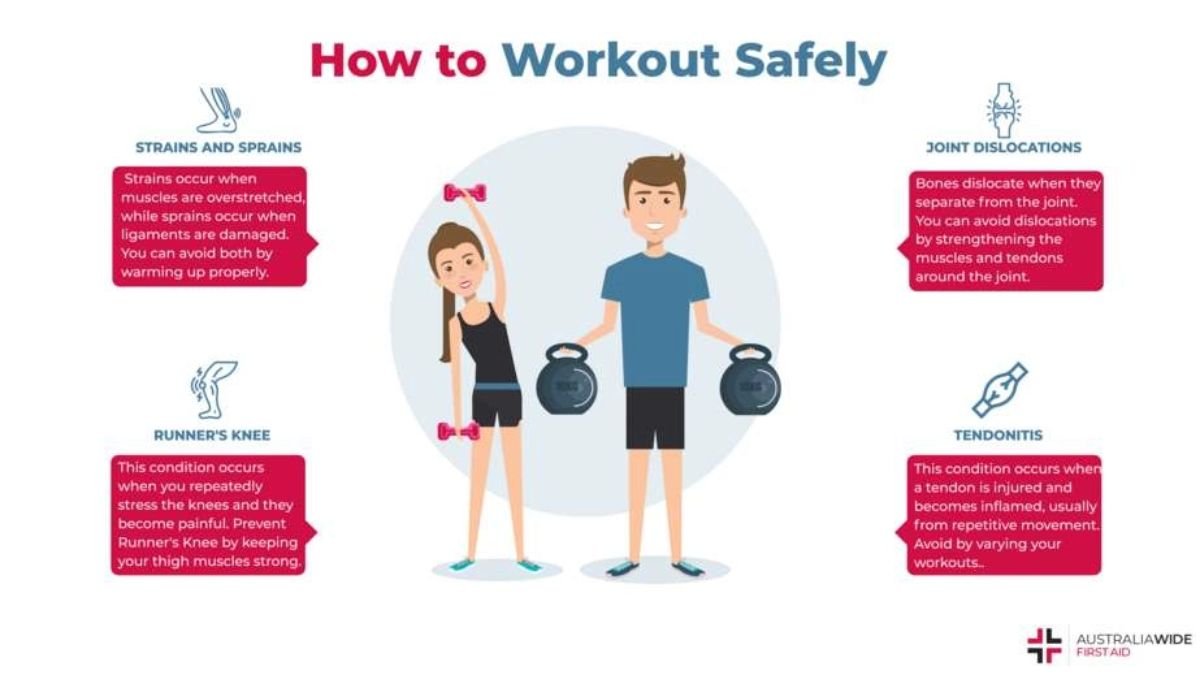
Before diving into prevention strategies, it is essential to recognize the most common types of workout injuries. These can range from mild strains and sprains to more severe conditions that may require medical attention.
Sprains and Strains
Sprains occur when ligaments—tissues connecting bones at a joint—are stretched or torn. They commonly affect the ankles and knees, often resulting from improper landing techniques or sudden twists. On the other hand, strains involve injuries to muscles or tendons, the tissues connecting muscles to bones. These injuries often occur due to overstretching or overexerting muscles during activities like lifting weights or running.
Tendonitis
Tendonitis is an inflammation or irritation of a tendon, typically caused by repetitive motion or overuse. Common forms include achilles tendonitis and rotator cuff tendonitis. These conditions often arise when individuals do not allow adequate recovery time or perform exercises without proper form.
Fractures
Fractures, or broken bones, can occur due to excessive stress or trauma during high-impact exercises. Stress fractures, which are small cracks in bones, often result from repetitive force or overuse, particularly in activities like running, jumping, or cycling.
Dislocations
A dislocation occurs when bones are forced out of their normal position in a joint. This can happen during activities that involve sudden impacts or falls, such as contact sports or even slipping on a gym floor. Dislocations are serious injuries that often require medical intervention.
Common Causes of Workout Injuries
Understanding the underlying causes of workout injuries can help you take proactive measures to avoid them. Some prevalent factors contributing to workout injuries include:
Lack of Warm-Up and Cool-Down
One of the most overlooked aspects of any workout routine is the warm-up and cool-down phase. Failing to properly warm up can leave your muscles unprepared for strenuous activity, increasing the risk of strains and sprains. Likewise, skipping a cool-down period can lead to muscle tightness and increased soreness post-workout.
Poor Technique and Form
Using improper technique during exercises can lead to undue stress on joints and muscles, resulting in injuries. For example, lifting weights without maintaining proper form can strain the back, while running with incorrect posture can lead to knee or hip injuries.
Overtraining and Insufficient Recovery
Many fitness enthusiasts are often eager to see results and may push their bodies beyond their limits. Overtraining without allowing sufficient time for recovery can lead to fatigue, decreased performance, and increased susceptibility to injuries. It is vital to listen to your body and recognize the importance of rest days.
Inappropriate Footwear
Wearing the right shoes for your specific activity is crucial in providing adequate support and cushioning. Using worn-out or inappropriate footwear can lead to instability and increase the risk of injuries, particularly in activities that involve a lot of jumping or lateral movements.
Ignoring Pain and Discomfort
Ignoring pain during a workout can lead to exacerbating existing injuries. It is important to differentiate between normal discomfort associated with physical exertion and actual pain that could indicate an injury. If something feels wrong, it is advisable to stop and reassess rather than pushing through the pain.
Strategies for Preventing Workout Injuries
Incorporating preventive measures into your fitness routine can significantly reduce the risk of injuries. Here are several strategies to consider:
Warm-Up Properly
A proper warm-up prepares your body for exercise by increasing blood flow to muscles, improving flexibility, and reducing the risk of injury. Aim for a dynamic warm-up that includes movements similar to the workout you plan to perform. For example, if you’re going for a run, include leg swings, lunges, and high knees to warm up your lower body.
Use Proper Technique
Educating yourself about proper techniques for each exercise is vital for preventing injuries. If you’re unsure of your form, consider working with a personal trainer or attending fitness classes. They can provide guidance and feedback to ensure you are using the correct posture and technique, especially for complex movements.
Gradually Increase Intensity
Avoid the temptation to jump into high-intensity workouts right away. Gradually increasing the intensity, duration, and frequency of your workouts allows your body to adapt to the demands placed upon it. This approach minimizes the risk of overuse injuries, especially if you are returning to exercise after a break.
Invest in Quality Footwear
Choosing the right footwear tailored to your specific activity can greatly impact your performance and injury risk. Ensure that your shoes fit well, provide adequate support, and are designed for the type of exercise you are engaging in. Replace them regularly, as worn-out shoes can compromise your stability and increase the risk of injury.
Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to your body’s signals and recognize when you need to rest or modify your workout. Fatigue, pain, and discomfort are signs that your body may require additional recovery time. Ignoring these signals can lead to more severe injuries that could sideline you for an extended period.
Incorporate Cross-Training
Incorporating a variety of exercises into your routine, known as cross-training, can help prevent overuse injuries. By engaging different muscle groups and varying the types of activities you perform, you reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries. For example, mixing running with swimming, cycling, or strength training can provide a balanced approach to fitness.
What to Do if You Experience an Injury
Despite your best efforts to prevent injuries, they can still occur. Knowing how to respond is crucial for minimizing damage and promoting recovery.
R.I.C.E. Method
If you experience a minor injury, consider using the R.I.C.E. method—Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation:
- Rest: Avoid using the injured area to prevent further damage.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes every few hours to reduce swelling and pain.
- Compression: Use elastic bandages or compression wraps to minimize swelling and provide support.
- Elevation: Elevate the injured area above heart level to help reduce swelling.
Seek Medical Attention
If your injury is severe, or if you experience persistent pain, swelling, or an inability to use the affected area, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment, including physical therapy if necessary.
Follow a Rehabilitation Program
After a workout injury, following a structured rehabilitation program is crucial for safe recovery. Engage in physical therapy or rehabilitation exercises as advised by your healthcare provider. This process can help restore strength, flexibility, and function to the injured area while minimizing the risk of re-injury.
Conclusion
Preventing workout injuries is an essential aspect of maintaining a consistent and effective exercise routine. By understanding the common types of injuries, their causes, and the strategies to prevent them, you can create a safer workout environment for yourself. Remember to prioritize proper warm-up and cool-down practices, focus on maintaining correct form, gradually increase your workout intensity, and listen to your body’s signals. In the event of an injury, utilizing the R.I.C.E. method and seeking professional medical advice can ensure proper recovery. By implementing these guidelines, you can enhance your workout experience, stay safe, and enjoy the numerous benefits of regular physical activity.